Discovery tactics to access the Kubernetes API Anonymously
This finding is used to indicate Kubernetes API commonly used to gain knowledge about the resources has been invoked by an anonymous user system:anonymous.
To simulate this we'll need to create a clusterrolebinding to bind clusterrole named anonymous-view to user named system:anonymous.
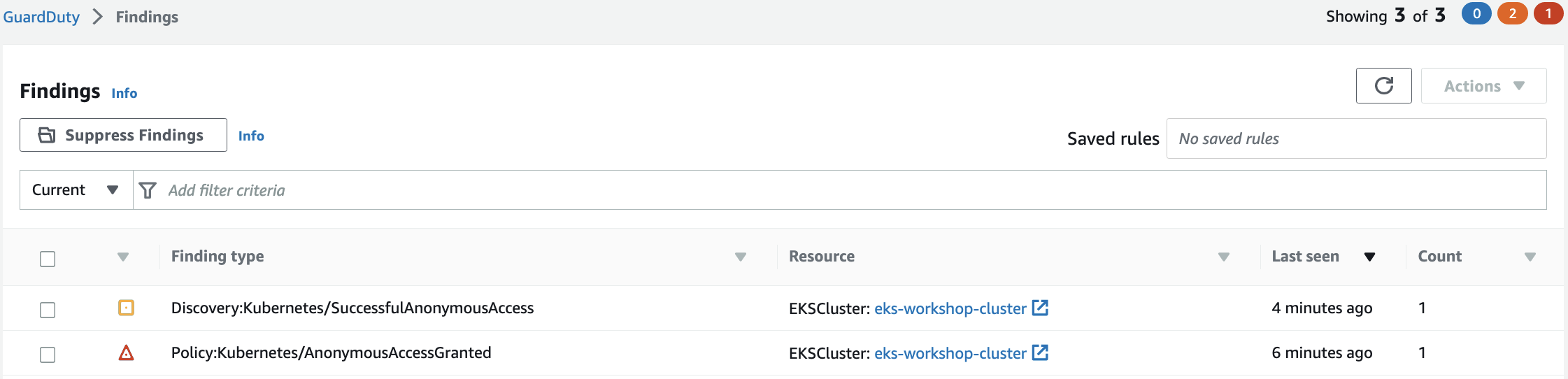
Note that the above rolebinding command will trigger Policy:Kubernetes/AnonymousAccessGranted finding in guard duty within few minutes.
Identify the API server URL of the cluster and run a HTTP get call for URI /api/v1/pods using curl. This is equivalent to running kubectl get pods -A -o json. The difference between kubectl and curl is that while using kubectl we'll be attaching an auth bearer token to authenticate, however while running curl we're not using any auth bearer token and skipping authentication and using system:anonymous for authorization.
Within a few minutes we'll see the finding Discovery:Kubernetes/SuccessfulAnonymousAccess in the GuardDuty portal.
Run the following command to delete the clusterrolebinding.